What is Celiac Disease?
According to medlineplus.gov , Celiac disease is an immune disease in which people can’t eat gluten because it will damage their small intestines. Celiac disease is a digestive disease that inhibits the small intestine’s ability to absorb nutrients from food. People who have celiac disease cannot tolerate a protein called gluten, which is found in wheat, rye, and barley. It is most often found in food, although it is also used as a binding agent in some medications and other everyday products.
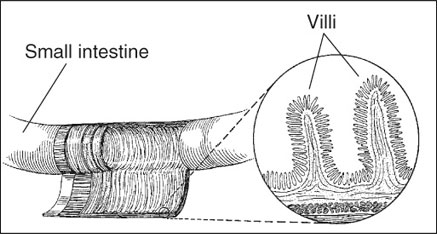
Celiac disease causes an immune system result that damages the villi, tiny, fingerlike protrusions that line the small intestine. The villi allow nutrients from food to be absorbed into the bloodstream. Without healthy villi, a person becomes malnourished, regardless of the quantity of food eaten.
Since the body’s immune response causes the damage, celiac disease is classified as an autoimmune disorder. It is also considered a malabsorption disease since it prevents nutrients from being absorbed. Other names for celiac disease include gluten-sensitive enteropathy, celiac sprue, and nontropical sprue.
Celiac disease is a genetic disease; most people who have it have at least one blood relative with the disease. The disease often becomes active after pregnancy, childbirth, surgery, viral infection or severe emotional stress.