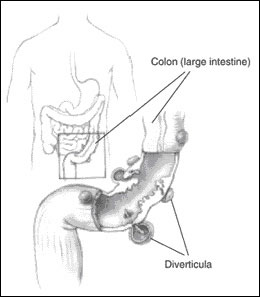
What is Diverticulosis?
Diverticulosis is a common condition that affects an estimated ten percent of Americans over the age of forty. Over time, small pouches in the lining of the colon begin to protrude and bulge out. Most of the time, this condition has no symptoms or adverse effects. If the pouches become infected and inflamed, however, the condition is known as diverticulitis. Up to 10 percent of people with diverticulosis develop diverticulitis.
Diverticulosis usually causes no discomfort or pain. In some instances, this condition can lead to cramps, bloating, and constipation. Diverticulitis, on the other hand, typically causes abdominal pain. One of the hallmarks of this condition is tenderness in the lower left side of the abdomen.
If you experience symptoms of diverticulosis and diverticulitis including persistent cramps, bloating, or constipation, contact us to schedule a consultation with Dr. Tabib. He can determine whether or not your symptoms are caused by this common condition and recommend the best course of treatment for you.